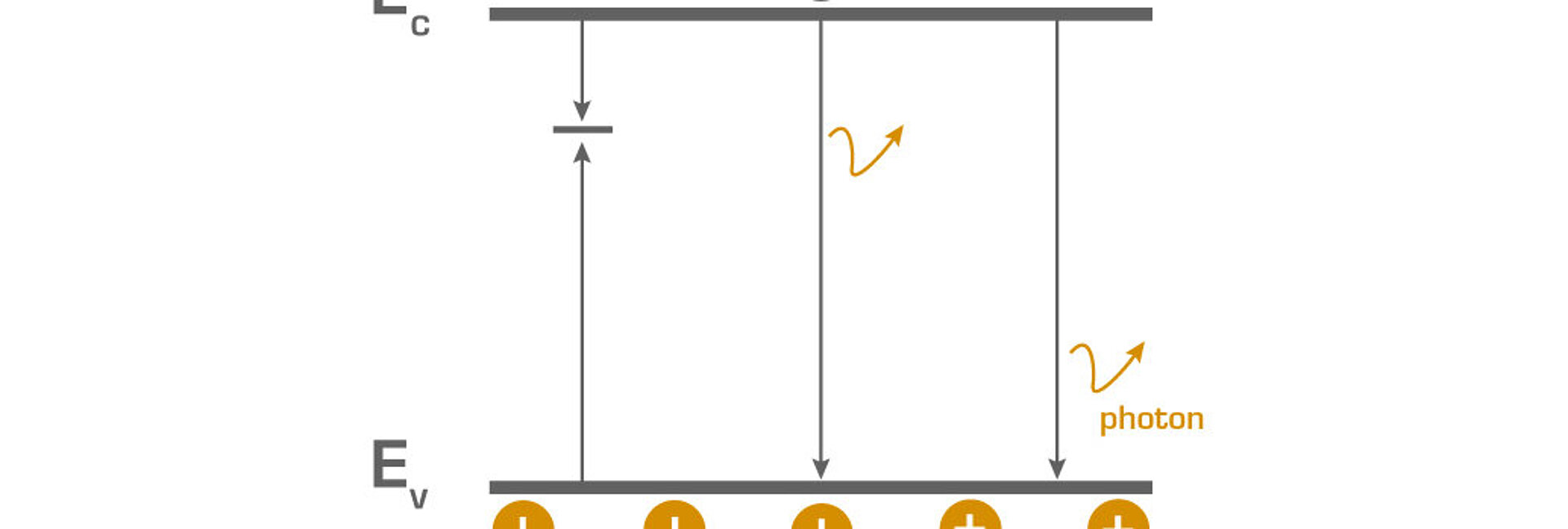
The measured effective lifetime is composed of the bulk lifetime and surface lifetime, which depends on the surface properties of a sample. Hence the surface has to be passivated, if you want to measure the bulk properties of your sample. If you want to investigate the surface passivation quality a FZ-Si wafer is recommendable, because the bulk recombination can be neglected.
\(\cfrac{1}{\tau_{eff}} = \cfrac{1}{\tau_{bulk}} + \cfrac{1}{\tau_{surface}}\)
Besides that the measured effective lifetime is dependent on the measuring method. For more details read:
[1] S. Rein, Lifetime Spectroscopy - A Method of Defect Characterization in Silicon for Photovoltaic Applications, Vol. 85 (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2005)
[2] D. K. Schroder, Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization, 2 ed. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998)