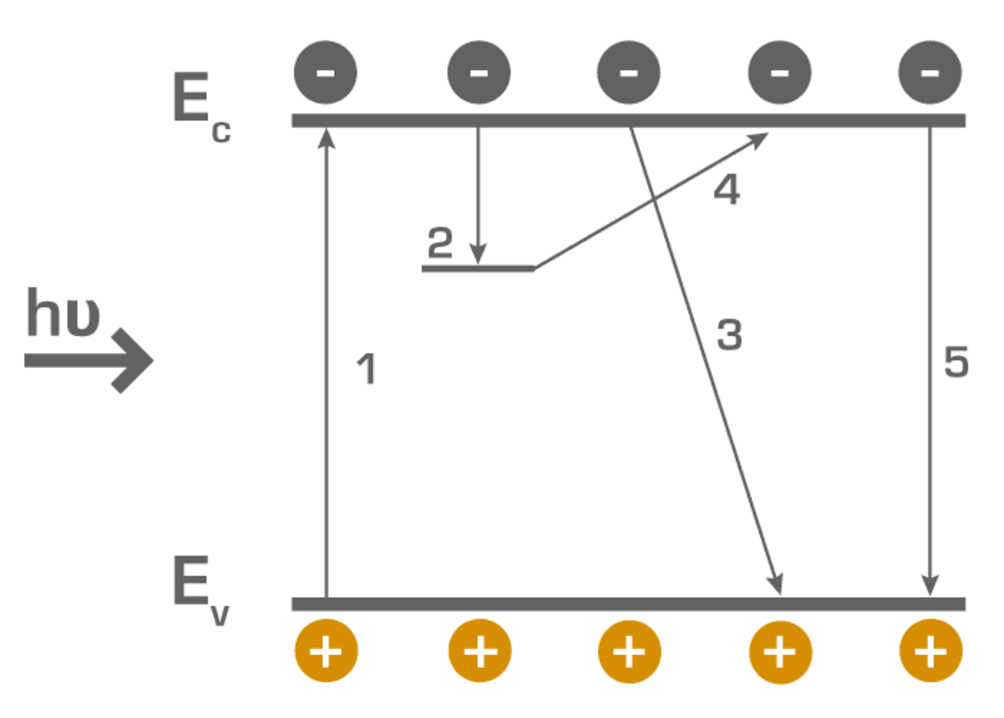
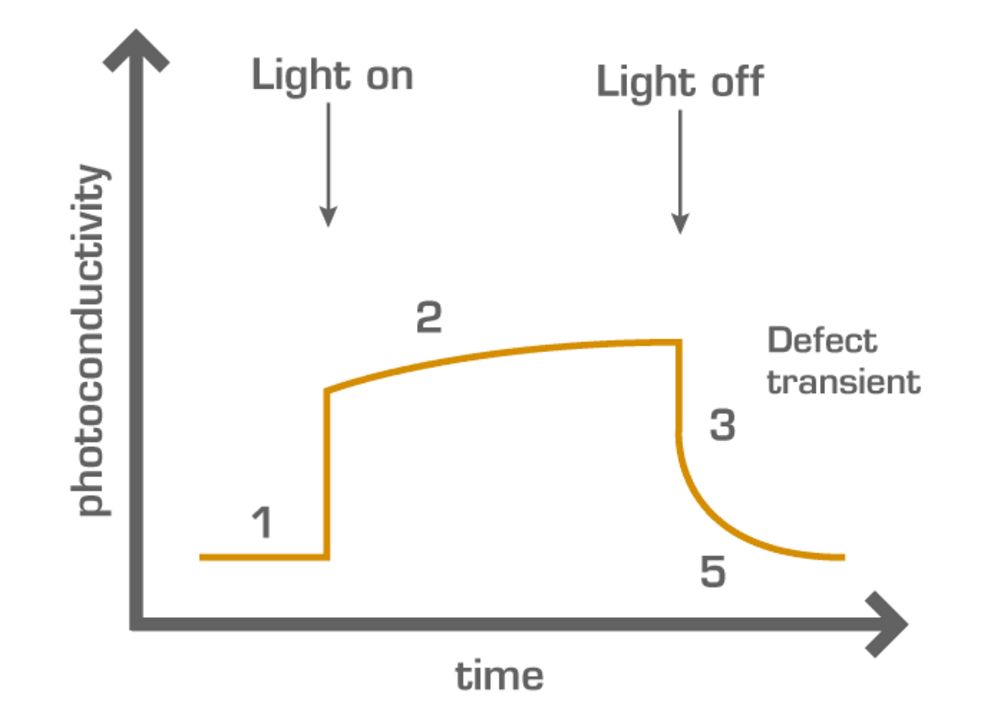
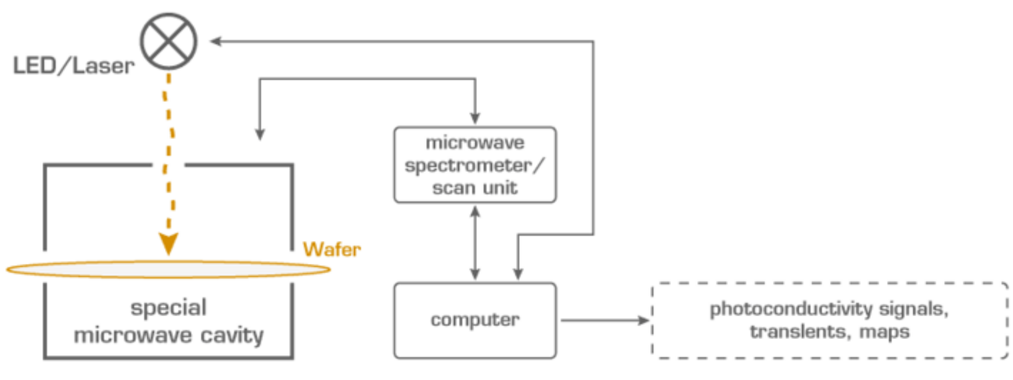
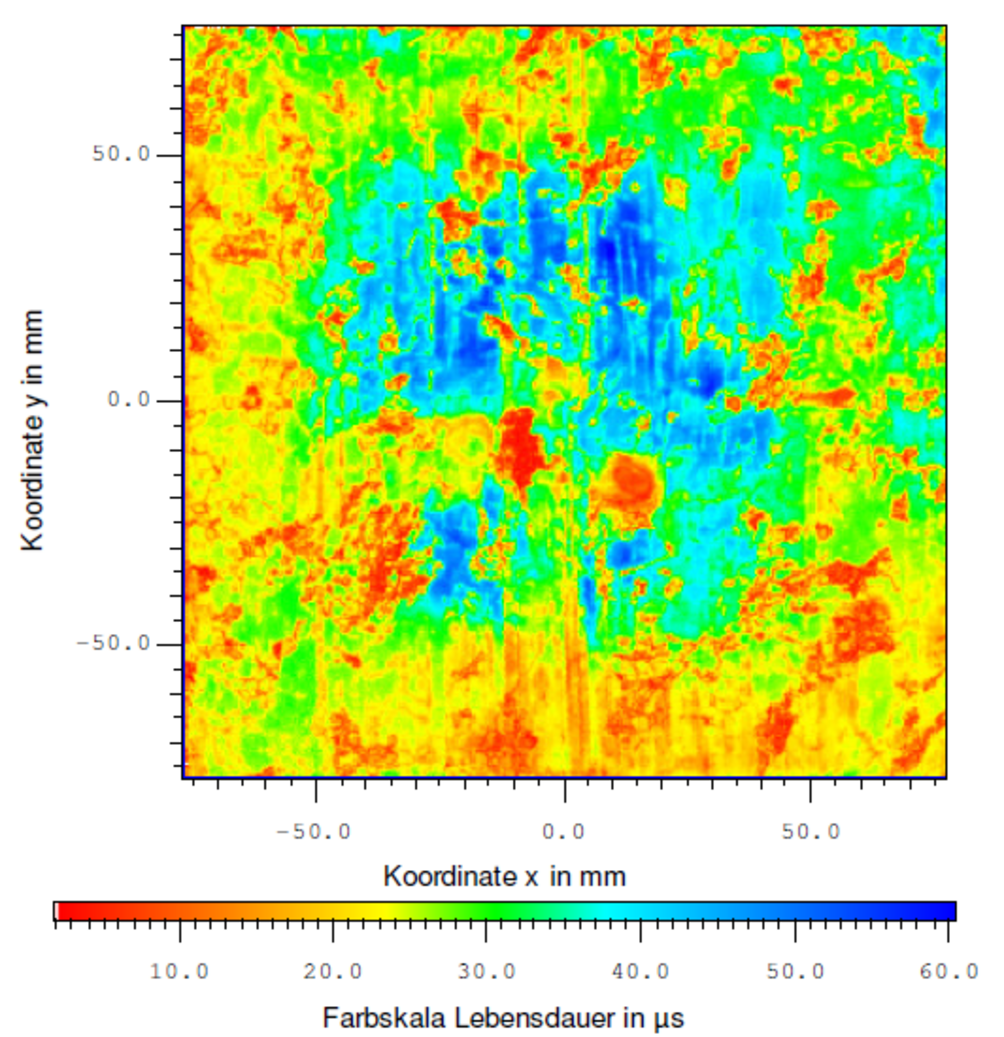
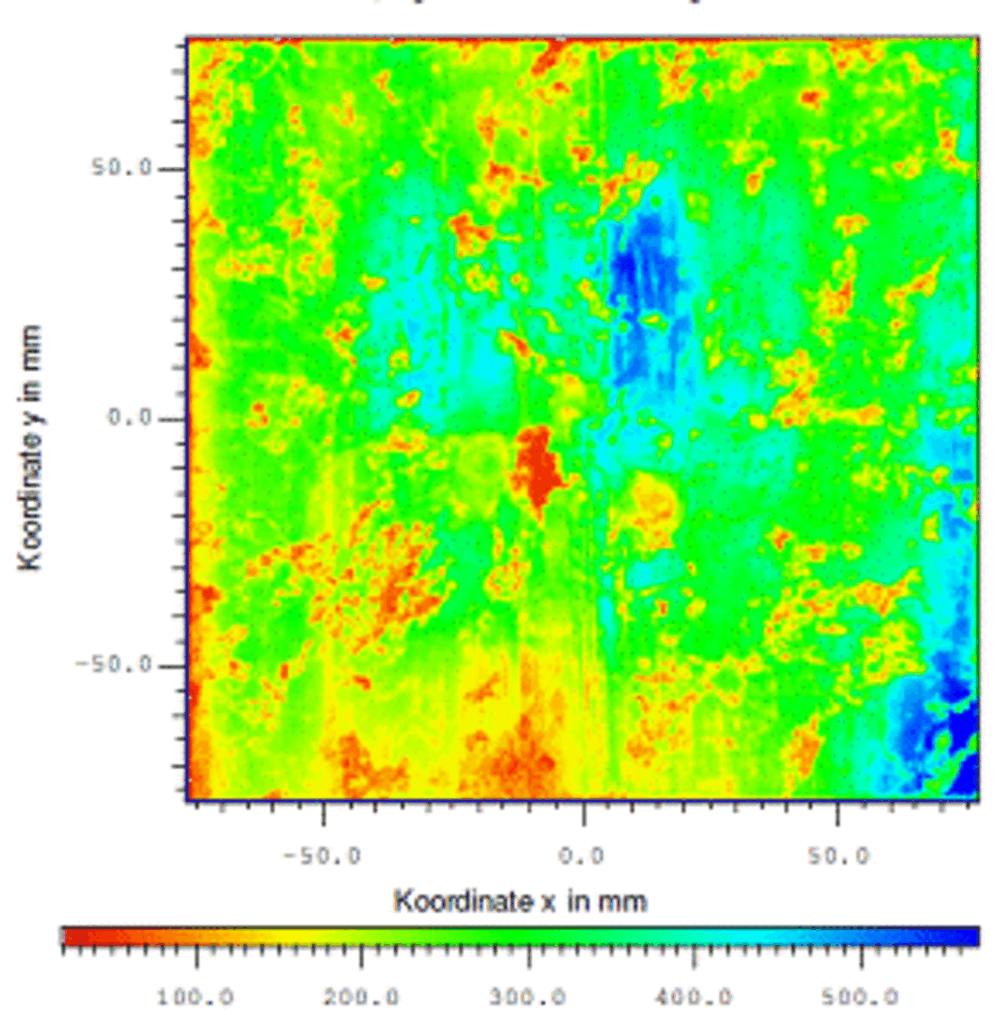
The novel method MDP is well suited for both, defect investigation by e.g. injection dependent minority carrier lifetime measurements, as well as mapping of wafers or even bricks for inline metrology. It exceeds his competitors µPCD (microwave detected photoconductivity decay) and QSSPC (quasi steady state photo conductance) in terms of sensitivity, resolution and speed.
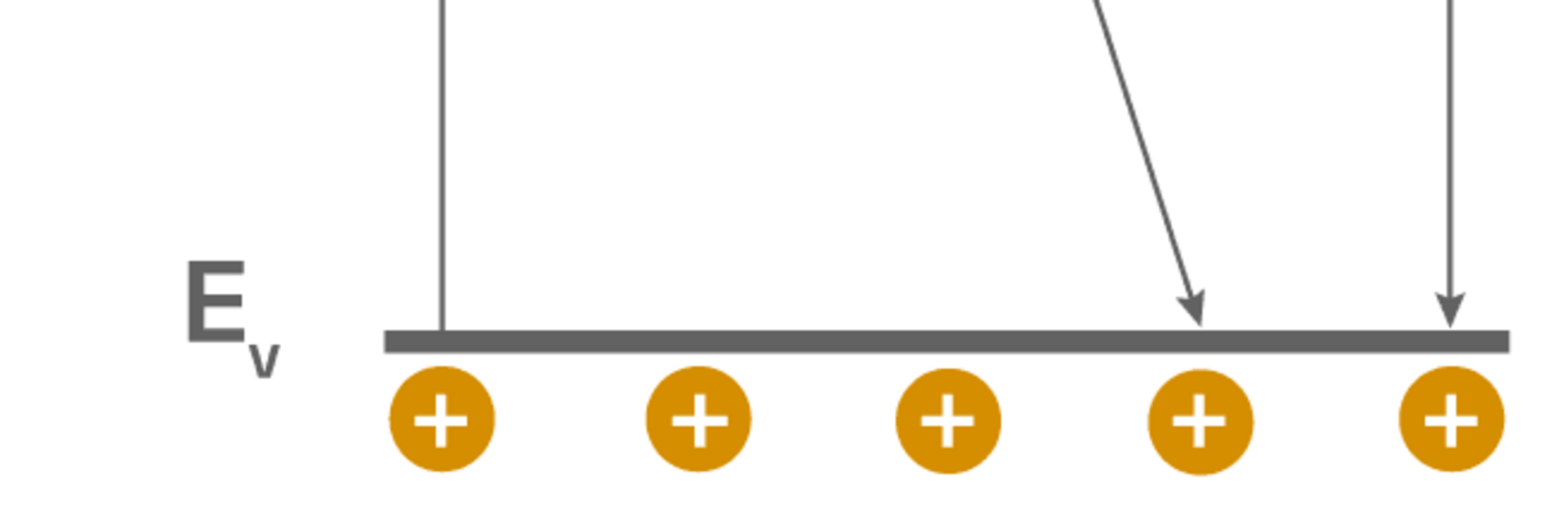

Microwave detected photoconductivity
The advanced method MDP is suited for defect investigation and mapping of wafers and ingotsWith its extraordinary sensitivity, resolution and speed MDP enables injection dependent measurements as well as mapping with a very high resolution.
Your cookie settings
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue without changing your settings, we'll assume that you are happy to receive all cookies from this website. Read more in our privacy policy.
Funktionale
Diese Cookies gewährleisten das korrekte Betreiben der Seite. Auch zustimmungsfreie Cookies oder First Party Cookies genannt.
The providers using cookies on this site are listed below. Where possible, you can choose to allow certain cookies on this site.
Cookies, which are required and set for the basic function of our site.
Cookies, which are needed and set for the use of the TYPO3 backend access.
Streaming-Dienste
Unsere Internetseite kann Elemente aus externen Quellen enthalten. Es wird darauf hingewiesen, dass wir keinen Einfluss darauf haben, dass Betreiber anderer Webseiten die geltenden Datenschutzbestimmungen einhalten. Weitere Informationen zu den einzelnen Anbietern finden Sie unter den detaillierten Informationen.
The providers using cookies on this site are listed below. Where possible, you can choose to allow certain cookies on this site.
Karten-Dienste
Unsere Internetseite kann Elemente aus externen Quellen enthalten. Es wird darauf hingewiesen, dass wir keinen Einfluss darauf haben, dass Betreiber anderer Webseiten die geltenden Datenschutzbestimmungen einhalten. Weitere Informationen zu den einzelnen Anbietern finden Sie unter den detaillierten Informationen.
The providers using cookies on this site are listed below. Where possible, you can choose to allow certain cookies on this site.